Draw curved arrows for acid-base reactions
Introduction:
One of the most important (if not the most important) reaction in organic chemistry is the acid-base reaction. Many reaction mechanisms contain multiple proton transfer steps. Therefore, if you can draw curved arrows for acid-base reactions then you already know parts of many mechanisms. Conversely, if you make mistakes in acid-base reactions then this mistake will be repeated in many of your reaction mechanisms.
How to:
The curved arrows for a general acid-base reaction is shown below. The acid-base reaction will occur between the most acidic proton and most basic lone pair. Note that the proton does not fly off by itself. The lone pair on the base grabs the proton.
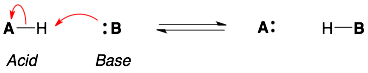
- There should be two curved arrows. This is because there is one bond formed (base grabbing the proton) and one bond broken (the acid releasing the proton).
- The arrows should flow in the same direction. Starting from the base and ending at the acid.
- The acid-base reaction should be charged balanced. The overall charge on the left-hand side of the equilibrium should be the same as the overall charge on the right-hand side of the equilibrium.
HINT: To get the arrows to go in the right direction. Think about the acid-base reaction as “the base grabs the acid”.
HINT: Acid-base reactions will have two curved arrows which will be head-to-tail (i.e. the go in the same direction).
Examples:
